|
|
|


THE WIRELESS TECHNOLOGY
Who is Bluetooth?

Harald Blaatand "Bluetooth" II - King of Denmark 840-981
Harald Bluetooth was the Danish King who unified Denmark and Norway in the 10th century. This is one o two Runic stones erected in his capital city of Jelling (central Jutland). In the beginning Bluetooth was a project name only. Now Bluetooth is the official name of the technology. In May 2000, the Bluetooth promoter companies announced the availability of a new figure mark to be used along with Bluetooth applications. The new figure mark is based on the Bluetooth history as it is made up of the two runic characters "H" and "B" - short for "Harald Bluetooth".

The Bluetooth history
In 1994, Ericsson Mobile Communications initiated a study to investigate the feasibility of a low-power, low-cost radio interface between mobile phones and their accessories. The aim was to eliminate cables between mobile phones and PC cards, headsets and desktop devices, etc.
The study was a part of a larger project investigating multicommunication connected to the cellular network via cellular phones. The last link in such a connection should be a short-range radio link. As the project progressed, it became clear that applications involving a short-range radio link were unlimited.
In the beginning of 1997, Ericsson approached other manufactures of portable devices to kindle interest in the technology. For the system to succeed and be truly useful, a critical mass of portable devices must use the same short-range radio link technology.
The Bluetooth ™ wireless technology is set to revolutionize the personal connectivity marked by providing links between mobile computers, mobile phones and other portable handled devices, and connectivity to the Internet. The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), comprised of leaders in the telecommunications, computing, and industries, is driving development of the technology and bringing it to market. The Bluetooth SIG includes promoter companies 3Com, Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Microsoft, Lucent, Nokia, Motorola and Toshiba, and thousands of adopter companies.
The Bluetooth wireless technology
The Bluetooth wireless technology will be the fastest growing industry standard ever. In this section you will find an overview of the Bluetooth concept, its advantages and a summary on the development of the technology.
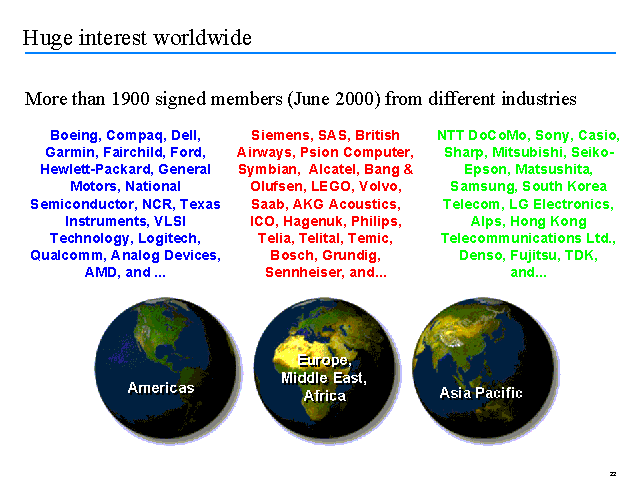
The Bluetooth Special Interest Group [SIG]
In Feb. 1998, a group to manage the new Bluetooth wireless technology was formed by representatives from Ericsson, Nokia, IBM, Toshiba and Intel (promoter group). This group became known as the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG). The intent was to create an open specification for a short-range, radio technology to replace cables.
Since the formation of Bluetooth SIG, thousands of companies have signed the Bluetooth Adopter agreements and joined the Bluetooth SIG. All adopters support the technology and they are committed to the development of Bluetooth product.
By signing a zero-cost agreement, the member companies qualify for a royalty-free license to build products based on the Bluetooth wireless technology. They also get access to the Bluetooth specifications and intensive training seminars. Additionally, the Bluetooth SIG provides a forum for vendor interaction and co-development opportunities.
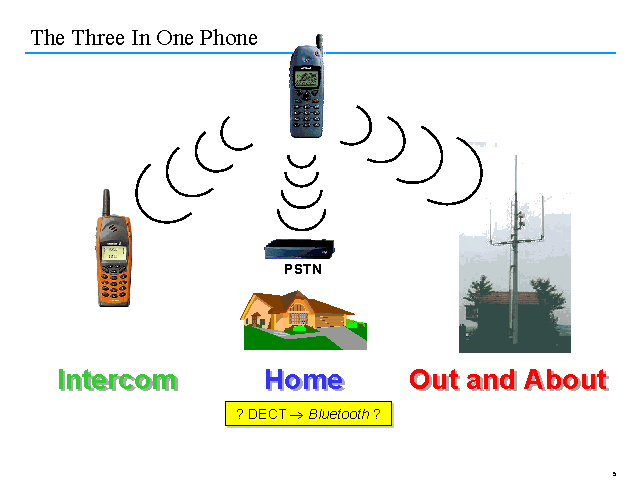
Bluetooth Applications
The potential applications of Bluetooth wireless technology are virtually unlimited. In this section has three major application areas: Data and Image, Internet and e-mail, and Voice Transmissions.

Bluetooth wireless technology
The Bluetooth solution answers the need for short-range wireless connectivity within three areas:
Bluetooth wireless technology is a system solution comprising hardware, software and interoperability requirements. The Bluetooth specifications specify the complete system.
Bluetooth wireless technology operates in a globally available 2.4 GHz ISM band, ensuring communication compatibility worldwide.
Data and Voice access points
Bluetooth wireless technology facilitates real-time voice and data transmissions. The technology makes it possible to connect any portable and stationary communication device as easily as switching on the lights.
For instance, surf the Internet and send e-mails on your portable PC or notebook regardless of whether you are wireless connected through a mobile phone or through a wire-bound connection (PSTN, ISDN, LAN, xDSL).
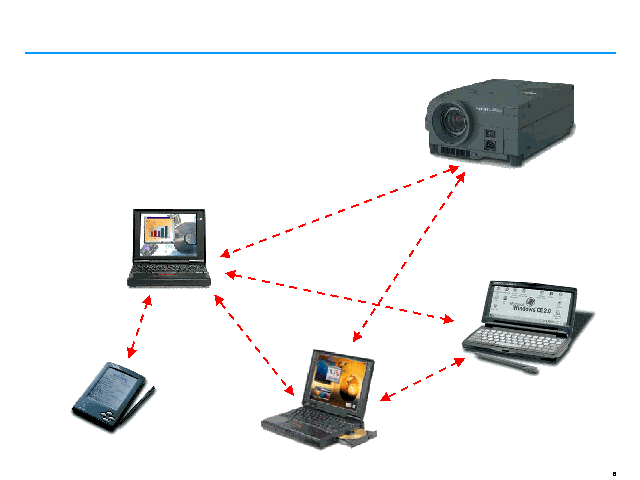
Cable replacement
Bluetooth wireless technology eliminates the need for numerous, often proprietary, cable attachment for connection of practically and kind of communication device. Connections are instant and they are maintained even when devices are not within line of sign. The range of each radio is approximately 10 meters, but it can be extended to 100 meters with an optional amplifier.

Back to Top
Ad hoc networking
A device equipped with a Bluetooth radio establishes instant connection to another Bluetooth radio as soon as it comes into range.
Since Bluetooth wireless technology supports both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint connections, several piconets can be established and linked together ad hoc. The Bluetooth topology is best described as a multiple piconet structure.